A형 필수 알고리즘을 체계적으로 배우고 싶다면? (인프런 바로가기)

참고
- 우선순위 큐 응용 (1) - 두 개의 heap을 이용하여 중앙값 찾기
- 우선순위 큐 응용 (2) - 최댓값, 최솟값 동시에 관리하기
- 우선순위 큐 임의 원소 삭제 최적화
Indexed Priority Queue, Heap - 삭제 구현, 최적화
이전 글에서는 우선순위 큐의 임의 원소 삭제에 O(NlogN)의 비용을 O(N) + O(logN) ≒ O(N)으로 줄였다.
이제 memoization을 이용하여 O(N) + O(logN)을 O(1) + O(logN) ≒ O(logN)으로 줄여보자.
아이디어는 다음과 같다.
deleteId 함수에서 delhn = findIndex(id);를 delhn = heapIdx[id]; 로 변경하면 된다.
heapIdx는 int 배열이며, heapIdx[id] = id의 현재 heap index를 저장하고 있다.
typedef struct st
{
int value;
int id;
}HEAP;
HEAP heap[16];
int heapIdx[16]; /* id가 heap의 어느 위치에 있는지 저장할 배열 */
int hn;
heapIdx에 현재 id가 heap의 어디에 위치해있는지 저장/갱신하기 위해 push 함수를 다음처럼 바꾼다.
void push(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int value, int id, int* heapIdx)
{
register HEAP tmp;
heap[++hn].value = value;
heap[hn].id = id;
heapIdx[id] = hn; /* id에 현재 hn을 저장 */
for (register int i = hn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isMin(heap[i / 2], heap[i])) break;
tmp = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
/* heapIdx 갱신 */
heapIdx[heap[i / 2].id] = i / 2;
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
}
}최초로 heapIdx[id]는 현재 heap에 push에 의해 결정된 hn이 된다.
현재 heap[i / 2]의 id는 i / 2가 될 것이고, heap[i]의 id는 i가 되므로 위와 같이 갱신하면 된다.
마찬가지로 pop도 아래처럼 갱신을 추가하자.
HEAP pop(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int* heapIdx)
{
register HEAP tmp, ret;
ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap[hn];
heap[hn].value = 0x7fff0000;
heap[hn--].id = 0x7fff0000;
for (register int i = 1; i * 2 <= hn;)
{
if (isMin(heap[i], heap[i * 2]) && isMin(heap[i], heap[i * 2 + 1])) break;
else if (isMin(heap[i * 2], heap[i * 2 + 1]))
{
tmp = heap[i * 2];
heap[i * 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
/* heapIdx 갱신 */
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i * 2].id] = i * 2;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heap[i * 2 + 1];
heap[i * 2 + 1] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
/* heapIdx 갱신 */
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i * 2 + 1].id] = i * 2 + 1;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}pop과 push의 함수에 int* heapIdx가 추가하는 것을 잊지 말자.
여기까지 구현했다면, 이전 글의 input 그대로 다시 pop해보자.
HEAP pop(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int* heapIdx);
void push(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int value, int id, int* heapIdx);
int main(void)
{
int input[] = { 6, 5, 3, 5, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 5, 6, 7, 0 }; /* 점수 input */
int size = sizeof(input) / sizeof(int);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) push(heap, hn, input[i], i + 1);
return 0;
}
그러면 아래와 같은 heap과 heapIdx가 완성된다.
id = 1부터 시작하므로 heapIdx[0] = 0이다.

위의 그림에서 heapIdx[3] = 5임을 알 수 있고, 실제 그림에서도 5번째 heap에 id = 3이 존재한다.
다른 id들도 heapIdx에 자신의 위치가 제대로 저장되어있는지 직접 확인해보자.
이제 deleteId를 수정하자.
delhn은 heapIdx[id]로 O(1)만에 찾을 수 있다.
그리고 deleteId의 delhn부터 heap을 갱신하는 코드에도 heapIdx 갱신을 추가하면 된다.
// int findIndex(int id);
int deleteId(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int id, int* heapIdx)
{
HEAP tmp;
int ret;
int delhn = heapIdx[id]; // findIndex(id);
ret = heap[delhn].value;
heap[delhn].value = -1;
for (int i = delhn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isMin(heap[i / 2], heap[i])) break;
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = tmp;
/* heapIdx 갱신 */
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i / 2].id] = i / 2;
}
pop(heap, hn, heapIdx);
return ret;
}
바뀐 deleteId로 id = 3을 제거하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나온다. (이전과 같은 결과이다.)
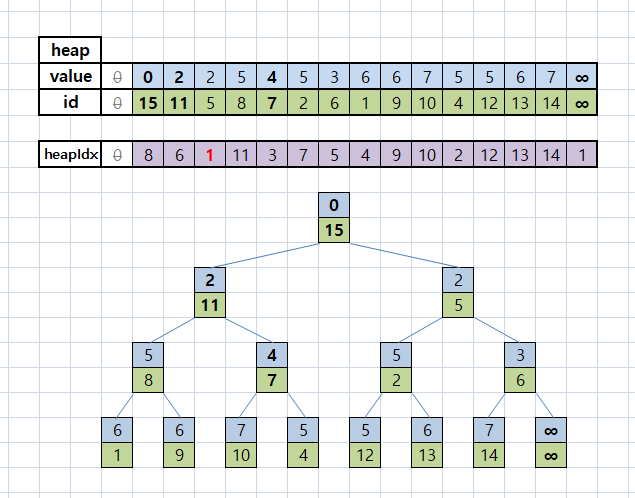
heapIdx[3] = 1로 가장 최근에 갱신된 내용이 남아있게 된다.
id = 3은 존재하지 않으므로, heapIdx[3]을 굳이 고칠 필요는 없다.
(문제 조건에 따라 id = 3이 존재하는지 묻는다면, 0이나 -1로 바꾸는 코드를 추가하면 된다.)
갱신된 heap도 여전히 heapIdx[id]가 id의 위치를 잘 가르키는지 직접 확인해보자.
최종 코드는 아래와 같다.
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct st
{
int value;
int id;
}HEAP;
HEAP heap[16];
int heapIdx[16]; /* id가 heap의 어느 위치에 있는지 저장할 배열 */
int hn;
int isMin(HEAP a, HEAP b)
{
if (a.value < b.value) return 1;
else if (a.value == b.value && a.id < b.id) return 1;
return 0;
}
void output(HEAP* heap)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++)
{
printf("%d (id : %d) ", heap[i].value, heap[i].id);
if ((i & (i + 1)) == 0) putchar('\n');
}
putchar('\n');
}
void outputHeapIdx(int* heapIdx)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) printf("%d ", heapIdx[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
HEAP pop(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int* heapIdx)
{
register HEAP tmp, ret;
ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap[hn];
heap[hn].value = 0x7fff0000;
heap[hn--].id = 0x7fff0000;
for (register int i = 1; i * 2 <= hn;)
{
if (isMin(heap[i], heap[i * 2]) && isMin(heap[i], heap[i * 2 + 1])) break;
else if (isMin(heap[i * 2], heap[i * 2 + 1]))
{
tmp = heap[i * 2];
heap[i * 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i * 2].id] = i * 2;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heap[i * 2 + 1];
heap[i * 2 + 1] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i * 2 + 1].id] = i * 2 + 1;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
void push(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int value, int id, int* heapIdx)
{
register HEAP tmp;
heap[++hn].value = value;
heap[hn].id = id;
heapIdx[id] = hn;
for (register int i = hn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isMin(heap[i / 2], heap[i])) break;
tmp = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i / 2].id] = i / 2;
}
}
int deleteId(HEAP* heap, int& hn, int id, int* heapIdx)
{
HEAP tmp;
int ret;
int delhn = heapIdx[id]; // findIndex(id);
ret = heap[delhn].value;
heap[delhn].value = -1;
for (int i = delhn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isMin(heap[i / 2], heap[i])) break;
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = tmp;
heapIdx[heap[i].id] = i;
heapIdx[heap[i / 2].id] = i / 2;
}
pop(heap, hn, heapIdx);
return ret;
}
int main(void)
{
int input[] = { 6, 5, 3, 5, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 5, 6, 7, 0 };
int size = sizeof(input) / sizeof(int);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) push(heap, hn, input[i], i + 1, heapIdx);
printf("%d\n", deleteId(heap, hn, 3, heapIdx));
output(heap); printf("\n");
outputHeapIdx(heapIdx);
return 0;
}'알고리즘 > [PRO] 삼성 SW 역량 테스트 B형' 카테고리의 다른 글
| BOJ 20920 : 영단어 암기는 괴로워 (우선순위 큐 갱신 + Hash Table) (0) | 2021.03.21 |
|---|---|
| BOJ 18139 : Rush Hour Puzzle (해시, 2차원 배열 탐색) (9) | 2021.03.18 |
| Indexed Priority Queue - 우선순위 큐의 임의 원소 삭제 (1) | 2021.03.13 |
| 해시 응용 : 2차원 배열 탐색 (5) | 2021.03.09 |
| 데이터의 추가, 삭제, 수정, 검색 - 해시 테이블 응용 (0) | 2021.02.28 |




댓글