참고
- 폴더, 파일 관리 함수 정리 with sys/stat.h, dirent.h, fstream
isDirectory - 폴더 / 파일 체크 함수
getAllFilePath - 해당 경로를 모두 읽어오는 함수
deleteDirectoryFiles - 폴더, 파일 삭제 함수
deleteAllDirectoryFiles - 모든 폴더, 파일 삭제 함수
fileCopy - 파일 복사 함수
numOfDigits - 자릿수를 세는 함수
padStart - 자릿수의 빈칸을 앞부분부터 특정 문자로 채우는 함수
split - 특정 문자열 기준으로 분해하는 함수
getExtension - 파일의 확장자를 얻는 함수
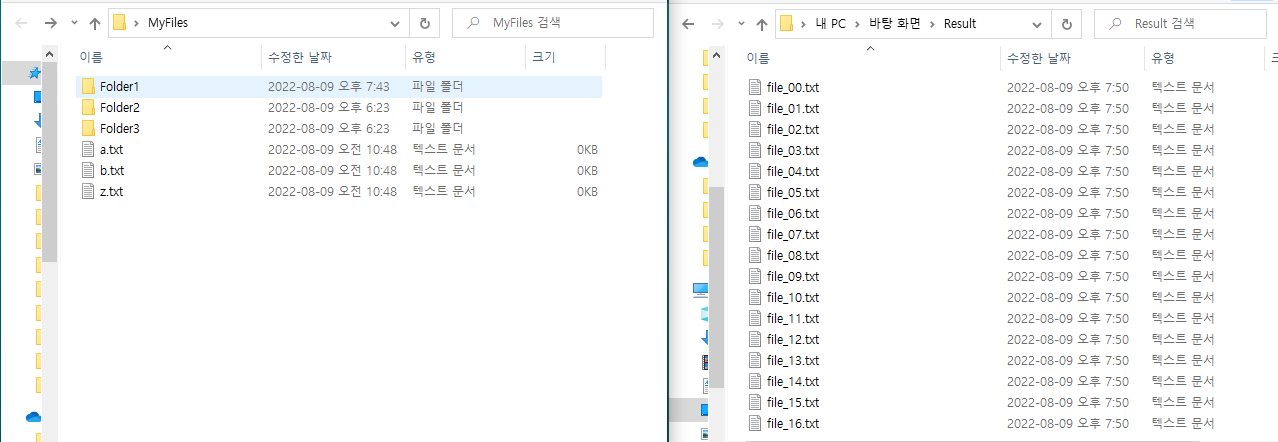
아래와 같이 MyFiles 폴더가 있다고 하자.
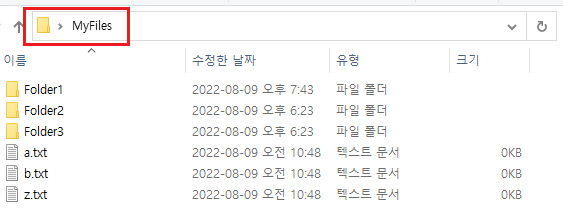
여기에 있는 파일들을 한꺼번에 하나로 통합하고 싶다.
직접 복사 / 붙여넣기를 해도 되지만,
폴더에 있는 파일들이 중복된 이름이 많은 경우에는 일일이 이름을 바꿔야 한다.
예를 들어 MyFiles의 Folder1에 a, b, z 파일이 있고, 또 그 안에 하위 폴더에도 같은 이름의 파일이 있다.
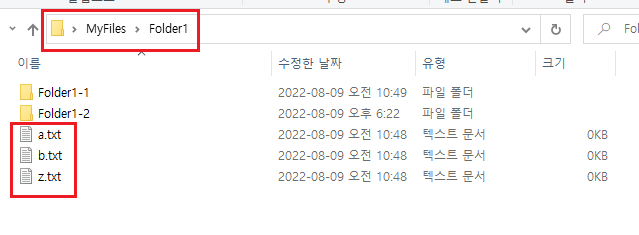
하위 폴더의 하위 폴더에도 a, b, z 파일이 있어 하나로 통합하기 번거롭다.
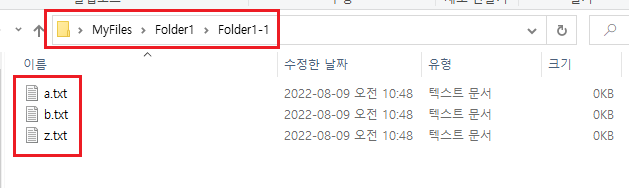
해당 폴더는 아래와 같다.
MyFiles - Folder1, 2, 3 / a, b, z
Folder1 - a, b, z
Folder1 - Folder1-1 - a, b, z
Folder1 - Folder1-2 - a, b, c
Folder2 - a, b, c
Folder3 - a, b
여기에 있는 모든 파일 a, b, c, z(= 17개)를 아래와 같이 Result 폴더에 합치자.
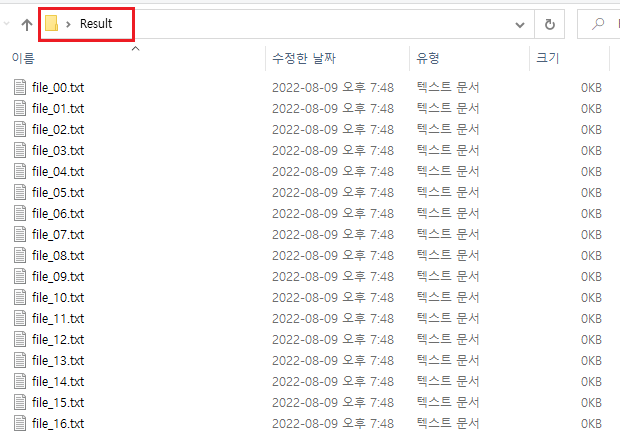
순서는 폴더 / 파일 구분 없이 이름 순으로 찾게 된다.
먼저 해당 폴더의 폴더 / 파일을 모두 훑은 후, 다시 폴더를 탐색한다.
따라서 번호가 매겨지는 순서는 아래와 같은 순서가 된다.
MyFiles - Folder1, 2, 3 / a(00), b(01), z(02)
Folder1 - a(03), b(04), z(05)
Folder1 - Folder1-1 - a(06), b(07), z(08)
Folder1 - Folder1-2 - a(09), b(10), c(11)
Folder2 - a(12), b(13), c(14)
Folder3 - a(15), b(16)
위의 첨부 파일에 위의 순서대로 파일에 번호를 체크해뒀으니, Merge한 후에 순서가 맞는지 확인해보자.
필요한 함수를 하나씩 살펴보자.
isDirectory - 폴더 / 파일 체크 함수
전체 경로를 주면 파일인지 폴더인지 검사한다.
#define ERROR (-1)
#define WINDOW_FILE (0)
#define DIRECTORY (1)
int isDirectory(string fullPath)
{
int ret;
_finddatai64_t fileData;
const char* fp = fullPath.c_str();
if (_findfirsti64(fp, &fileData) == ERROR) ret = ERROR;
else
{
if (fileData.attrib & _A_SUBDIR) ret = DIRECTORY;
else ret = WINDOW_FILE;
}
_findclose(ret);
return ret;
}
vs를 출력하면 아래의 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
해당 폴더의 파일 / 폴더를 사전 순으로 먼저 탐색 후, 사전 순으로 먼저인 폴더를 탐색한다.

getAllFilePath - 해당 경로를 모두 읽어오는 함수
경로를 넘겨주면 해당 경로에 존재하는 모든 파일 / 폴더의 경로를 vs에 저장한다.
순서는 위에 정의한 대로 폴더 → 폴더 내부의 폴더 → ... → 파일 순으로 경로가 저장된다.
void getAllFilePath(string path, vector<string>& vs)
{
FILE* pipe = NULL;
string prompt = "dir /s /b " + path;
char buf[500];
pipe = _popen(prompt.c_str(), "rt");
if (pipe == NULL)
{
printf("%Pipe is Null\n");
return;
}
while (!feof(pipe))
{
if (fgets(buf, 500, pipe) != NULL)
{
int len = 0;
for (; buf[len++];);
if (buf[len - 2] == 10 /* Line Feed */) buf[len - 2] = 0;
vs.push_back(string(buf));
}
}
_pclose(pipe);
}deleteDirectoryFiles - 폴더, 파일 삭제 함수
deleteAllDirectoryFiles - 모든 폴더, 파일 삭제 함수
void deleteDirectoryFiles(string path)
{
if (isDirectory(path) == DIRECTORY) _rmdir(path.c_str());
else if (isDirectory(path) == WINDOW_FILE) _unlink(path.c_str());
}
void deleteAllDirectoryFiles(string path)
{
if (isDirectory(path) != DIRECTORY) return;
vector<string> allPath;
vector<string>::iterator inverse, iter;
getAllFilePath(path, allPath);
if (allPath.size())
{
for (inverse = allPath.begin(); inverse != allPath.end(); inverse++);
--inverse;
for (iter = inverse; iter != allPath.begin(); iter--) deleteDirectoryFiles(*iter);
deleteDirectoryFiles(*iter);
}
_rmdir(path.c_str());
}fileCopy - 파일 복사 함수
src 파일을 dest에 복사한다.
int fileCopy(const char* src, const char* dest)
{
FILE* fsrc;
FILE* fdest;
char buff[1024];
size_t n_size;
if (!strcmp(src, dest)) return -1; // 원본 사본 파일이 동일하면 에러
fsrc = fopen(src, "rb"); //원본 파일 열기
if (fsrc == NULL) return -2;
fdest = fopen(dest, "wb"); //대상 파일 열기
if (fdest == NULL)
{
fclose(fsrc);
return -3;
}
while (0 < (n_size = fread(buff, 1, sizeof(buff), fsrc)))
{
if (0 == fwrite(buff, 1, n_size, fdest))
{
fclose(fsrc);
fclose(fdest);
unlink(dest); //에러 파일 지우고 종료
return -4;
}
}
fclose(fsrc);
fclose(fdest);
return 0;
}numOfDigits - 자릿수를 세는 함수
파일의 번호를 붙이기 위해 필요하다.
만약 파일이 123개라면
001 ~ 123이 되어야 하므로 자릿수가 3이라는 것을 알아야 한다.
int numOfDigits(int number)
{
int ret = 0;
while (number)
{
ret++;
number /= 10;
}
return ret;
}padStart - 자릿수의 빈칸을 앞부분부터 특정 문자로 채우는 함수
파일이 123개라면 파일이름이 000, 001, 002, ...로 붙는다. pad = '0'을 주면 자릿수만큼 0을 채운다.
string padStart(int number, int padSize, char pad)
{
string strNum = to_string(number);
string ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < padSize - strNum.size(); i++) ret = ret + pad;
return ret + strNum;
}split - 특정 문자열 기준으로 분해하는 함수
링크 참고.
getExtension - 파일의 확장자를 얻는 함수
a.txt라면 txt를 리턴한다. 즉, 확장자를 리턴한다.
string getExtension(string str)
{
vector<string> vs = split(str, '.');
return vs[vs.size() - 1];
}main 분석
위의 함수들을 이용하여
1. RESULT_PATH(결과를 저장할 경로)를 모두 삭제(안에 있는 파일을 삭제)하고, 다시 새로 만든다.
2. PATH(파일을 복사할 루트 폴더)에서 모든 파일 / 폴더의 경로를 files에 저장한다.
3. isDirectory로 파일만 센다.
4. 파일의 개수를 바탕으로 몇 자리 수인지, pad를 얼마나 채울지 정한다.
5. 파일인 경우 순서대로 복사한다. (destPath에 파일을 복사하고, changeName으로 변경한다.
int main()
{
cout << "Start" << endl;
deleteAllDirectoryFiles(RESULT_PATH);
_mkdir(RESULT_PATH);
vector<string> files;
getAllFilePath(PATH, files);
vector<string>::iterator it = files.begin();
int fileCount = 0;
while (it != files.end())
{
if (isDirectory(*it) == WINDOW_FILE) fileCount++;
it++;
}
it = files.begin();
int padSize = numOfDigits(fileCount);
int fileIndex = 0;
while (it != files.end())
{
if (isDirectory(*it) == WINDOW_FILE)
{
cout << *it << endl;
vector<string> vs = split(*it, '\\');
string fileName = vs[vs.size() - 1];
string destPath = string(RESULT_PATH) + "\\" + fileName;
fileCopy(it->c_str(), destPath.c_str());
string changeName
= string(RESULT_PATH) +
"\\file_" + padStart(fileIndex++, padSize, '0') + "." + getExtension(fileName);
rename(destPath.c_str(), changeName.c_str());
}
it++;
}
return 0;
}
아래의 define에 원하는 폴더 경로를 넣어두자.
#define PATH "C:\\Users\\username\\Desktop\\MyFiles"
#define RESULT_PATH "C:\\Users\\username\\Desktop\\Result"
그러면 MyFiles의 모든 파일이 Result에 순서대로 저장된다.
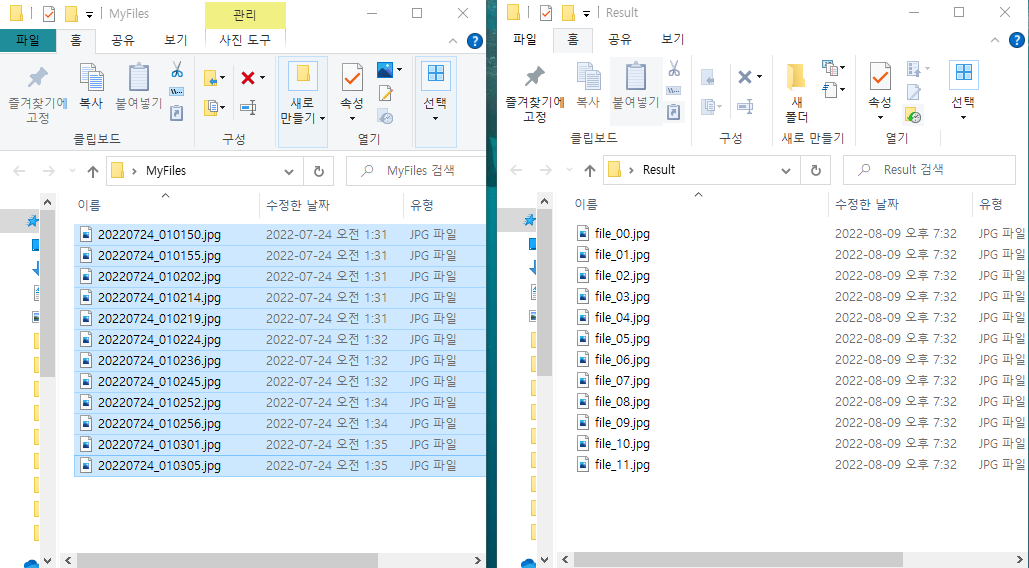
이러한 방식으로 원하는 파일이 이름은 엉망이지만 순서는 지켜져있는 경우(저장된 사진을 옮긴다거나 할 때)
파일의 이름을 정리하고 라벨링을 할 수 있다.
아래는 오늘 하루 찍은 사진 파일을 MyFiles 폴더에 옮긴 것이다.
숫자가 엉망이라서 정리하기 힘들 때 순서대로 라벨링을 붙여주었다.
changeName을 변경하면 원하는 파일 이름을 설정할 수 있다.
string changeName
= string(RESULT_PATH) +
"\\file_" + padStart(fileIndex++, padSize, '0') + "." + getExtension(fileName);
전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <io.h>
#include <direct.h>
using namespace std;
#define PATH "C:\\Users\\username\\Desktop\\MyFiles"
#define RESULT_PATH "C:\\Users\\username\\Desktop\\Result"
#define ERROR (-1)
#define WINDOW_FILE (0)
#define DIRECTORY (1)
int isDirectory(string fullPath)
{
int ret;
_finddatai64_t fileData;
const char* fp = fullPath.c_str();
if (_findfirsti64(fp, &fileData) == ERROR) ret = ERROR;
else
{
if (fileData.attrib & _A_SUBDIR) ret = DIRECTORY;
else ret = WINDOW_FILE;
}
_findclose(ret);
return ret;
}
void getAllFilePath(string path, vector<string>& vs)
{
FILE* pipe = NULL;
string prompt = "dir /s /b " + path;
char buf[500];
pipe = _popen(prompt.c_str(), "rt");
if (pipe == NULL)
{
printf("%Pipe is Null\n");
return;
}
while (!feof(pipe))
{
if (fgets(buf, 500, pipe) != NULL)
{
int len = 0;
for (; buf[len++];);
if (buf[len - 2] == 10 /* Line Feed */) buf[len - 2] = 0;
vs.push_back(string(buf));
}
}
_pclose(pipe);
}
void deleteDirectoryFiles(string path)
{
if (isDirectory(path) == DIRECTORY) _rmdir(path.c_str());
else if (isDirectory(path) == WINDOW_FILE) _unlink(path.c_str());
}
void deleteAllDirectoryFiles(string path)
{
if (isDirectory(path) != DIRECTORY) return;
vector<string> allPath;
vector<string>::iterator inverse, iter;
getAllFilePath(path, allPath);
if (allPath.size())
{
for (inverse = allPath.begin(); inverse != allPath.end(); inverse++);
--inverse;
for (iter = inverse; iter != allPath.begin(); iter--) deleteDirectoryFiles(*iter);
deleteDirectoryFiles(*iter);
}
_rmdir(path.c_str());
}
//이름 변경
int fileCopy(const char* src, const char* dest)
{
FILE* fsrc;
FILE* fdest;
char buff[1024];
size_t n_size;
if (!strcmp(src, dest)) return -1; // 원본 사본 파일이 동일하면 에러
fsrc = fopen(src, "rb"); //원본 파일 열기
if (fsrc == NULL) return -2;
fdest = fopen(dest, "wb"); //대상 파일 열기
if (fdest == NULL)
{
fclose(fsrc);
return -3;
}
while (0 < (n_size = fread(buff, 1, sizeof(buff), fsrc)))
{
if (0 == fwrite(buff, 1, n_size, fdest))
{
fclose(fsrc);
fclose(fdest);
unlink(dest); //에러 파일 지우고 종료
return -4;
}
}
fclose(fsrc);
fclose(fdest);
return 0;
}
int numOfDigits(int number)
{
int ret = 0;
while (number)
{
ret++;
number /= 10;
}
return ret;
}
string padStart(int number, int padSize, char pad)
{
string strNum = to_string(number);
string ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < padSize - strNum.size(); i++) ret = ret + pad;
return ret + strNum;
}
vector<string> split(string str, char delimiter)
{
vector<string> vs;
string temp;
for (int i = 0; !(str[i] == 13 /* Line Feed */ || str[i] == '\n' || str[i] == 0); i++)
{
if (str[i] == delimiter)
{
vs.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
continue;
}
temp.push_back(str[i]);
}
vs.push_back(temp);
return vs;
}
string getExtension(string str)
{
vector<string> vs = split(str, '.');
return vs[vs.size() - 1];
}
int main()
{
cout << "Start" << endl;
deleteAllDirectoryFiles(RESULT_PATH);
_mkdir(RESULT_PATH);
vector<string> files;
getAllFilePath(PATH, files);
vector<string>::iterator it = files.begin();
int fileCount = 0;
while (it != files.end())
{
if (isDirectory(*it) == WINDOW_FILE) fileCount++;
it++;
}
it = files.begin();
int padSize = numOfDigits(fileCount);
int fileIndex = 0;
while (it != files.end())
{
if (isDirectory(*it) == WINDOW_FILE)
{
cout << *it << endl;
vector<string> vs = split(*it, '\\');
string fileName = vs[vs.size() - 1];
string destPath = string(RESULT_PATH) + "\\" + fileName;
fileCopy(it->c_str(), destPath.c_str());
string changeName
= string(RESULT_PATH) +
"\\file_" + padStart(fileIndex++, padSize, '0') + "." + getExtension(fileName);
rename(destPath.c_str(), changeName.c_str());
}
it++;
}
return 0;
}
참고 : 유니티 C# version
'개발 > C, C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| N x N 2차원 배열 뒤집기, 회전하기 (Rotate, Flip 2D Array) (0) | 2022.11.27 |
|---|---|
| 100명의 죄수가 살아남을 확률을 높이기 위한 루프 전략 (Loop Strategy) (4) | 2022.09.24 |
| 원주율 Pi : 라이프니츠 공식 (Leibniz Formula for π) (0) | 2022.08.01 |
| 셔플 Shuffle - 카드 섞기 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.07.08 |
| 인터페이스 vs 추상 클래스 (Java, C++ 비교) (0) | 2022.02.05 |



댓글