shared_ptr은 포인팅 횟수를 계산해서 0이 되면 객체를 소멸하는 스마트 포인터이다.
아래 코드의 결과를 확인해보자.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <memory> // shared_ptr header
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class FOOD
{
private:
int price = 0;
public:
FOOD() { printf("FOOD created\n"); }
~FOOD() { printf("FOOD deleted\n"); }
virtual void printName() { cout << "FOOD Class" << endl; }
virtual void printPrice() { cout << this->price << endl; }
void printLine() { cout << "=================" << endl; }
};
int main(void)
{
cout << "start main\n" << endl;
shared_ptr<FOOD> myFood(new FOOD);
cout << "my count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
{
shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood(myFood);
//shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood;
//sharedFood = myFood;
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "sh count : " << sharedFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "sh address : 0x" << sharedFood.get() << endl;
}
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "my address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "\nend main\n" << endl;
return 0;
}
처음에 new FOOD로 myFood를 생성하였고,
share_ptr의 use_count 메서드로 현재 포인팅하는 포인터 개수가 1임을 알 수 있다.
다음 스코프에서 shareFood는 myFood로 생성하였고, 두 객체의 use_count가 모두 2임을 알 수 있다.
그리고 get 메서드를 통해 주소를 확인해보면 같은 포인터임을 알 수 있다.
스코프가 끝나서 shareFood에 참조할 수 없더라도, use_count가 1이기 때문에 객체는 소멸되지 않았다.
그리고 main문이 종료되면 FOOD 객체가 소멸되는 것을 알 수 있다.
그리고 shared_ptr의 아래의 코드는 아래와 같이 변경하여도 같은 동작을 한다.
//shared_ptr<FOOD> shareFood(myFood);
shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood;
sharedFood = myFood;
auto_ptr과 달리 myFood가 NULL이 되지 않는다.
reset 메서드를 이용하면 현재 참조하는 포인터를 즉시 삭제할 수 있다.
shared_ptr<FOOD> shareFood(myFood); 아래에 reset을 추가하고 end main 전에 myFood에 reset을 해보자.
{
shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood(myFood);
//shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood;
//sharedFood = myFood;
sharedFood.reset();
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "sh count : " << sharedFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "sh address : 0x" << sharedFood.get() << endl;
}
myFood.reset();
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "my address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "\nend main\n" << endl;
sharedFood의 use_count는 0이 되고, address는 NULL이 되었다.
myFood의 포인팅 횟수가 감소하였으므로 1이 된 것을 알 수 있다.
그리고 스코프 종료 후 myFood의 reset으로 main 종료 전에 FOOD deleted가 실행되었다.
count가 0이 되자마자 객체가 소멸된 것을 알 수 있다.
shared_ptr은 배열로 된 객체도 삭제할 수 있다.
단, 개발자가 삭제하는 함수를 직접 만들어서 등록해야 한다.
객체를 삭제하는 함수 deleteObjects를 만들어서 myFood를 생성할 때 넘겨주면 된다.
void deleteObjects(FOOD* foods)
{
cout << "delete array" << endl;
delete[] foods;
}
int main(void)
{
cout << "start main\n" << endl;
shared_ptr<FOOD> myFood(new FOOD[5], deleteObjects);
cout << "my count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
{
shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood(myFood);
//shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood;
//sharedFood = myFood;
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "sh count : " << sharedFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "sh address : 0x" << sharedFood.get() << endl;
}
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "my address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "\nend main\n" << endl;
return 0;
}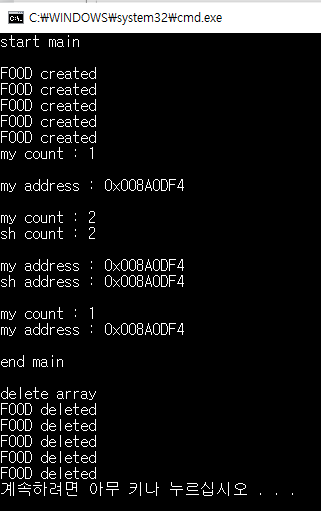
만들어진 5개의 객체가 모두 소멸되는 것을 알 수 있다.
shared_ptr이 auto_ptr을 완전 대체할 수 있으므로 shared_ptr을 사용하면 된다.
최종 코드는 아래를 참고하자.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <memory> // shared_ptr header
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class FOOD
{
private:
int price = 0;
public:
FOOD() { printf("FOOD created\n"); }
~FOOD() { printf("FOOD deleted\n"); }
virtual void printName() { cout << "FOOD Class" << endl; }
virtual void printPrice() { cout << this->price << endl; }
void printLine() { cout << "=================" << endl; }
};
void deleteObjects(FOOD* foods)
{
cout << "delete array" << endl;
delete[] foods;
}
int main(void)
{
cout << "start main\n" << endl;
shared_ptr<FOOD> myFood(new FOOD[5], deleteObjects);
cout << "my count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
{
shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood(myFood);
//shared_ptr<FOOD> sharedFood;
//sharedFood = myFood;
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "sh count : " << sharedFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "\nmy address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "sh address : 0x" << sharedFood.get() << endl;
}
cout << "\nmy count : " << myFood.use_count() << endl;
cout << "my address : 0x" << myFood.get() << endl;
cout << "\nend main\n" << endl;
return 0;
}'개발 > C, C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ 스마트 포인터 : unique_ptr (0) | 2021.10.16 |
|---|---|
| C++ 스마트 포인터 : weak_ptr (0) | 2021.10.14 |
| C++ 스마트 포인터 : auto_ptr (0) | 2021.10.10 |
| C++ 스마트 포인터 (Smart Pointer) (0) | 2021.10.03 |
| C++ - 형변환 연산자 (casting operators) (0) | 2021.08.26 |




댓글