참고
- https://www.vultr.com/resources/ipv4-converter/
- IPv4 Invalid Check
- IPv6 Invalid Check (+ 축약형)
- Integer to IPv4 String
- IPv4 String to Integer
- IPv4 String to Integer / Integer to IPv4 String with <arpa/inet.h>
- in_addr to IPv4 String / IPv4 String to in_addr with <arpa/inet.h>
- in6_addr to IPv6 String / IPv6 String to in6_addr with <arpa/inet.h>
- IPv4 to IPv6 with <arpa/inet.h>
IP Converter
https://www.vultr.com/resources/ipv4-converter/
위 링크의 IPv4 Converter에서 나오는 결과를 C++에서 구현해 보자.
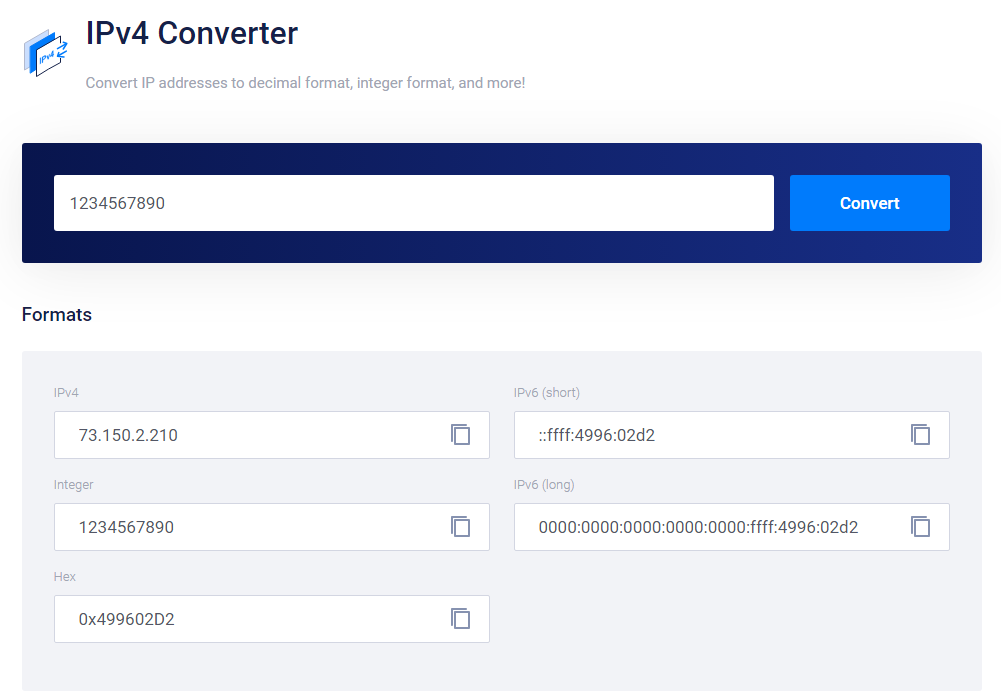
IPv4 Invalid Check
IPv4의 형식은 192.168.1.1 과 같은 형식이다.
1 ~ 3개의 숫자가 4번 반복되고 그 사이에 . 이 있다.
C++의 정규 표현식 라이브러리 regex를 이용해서 IPv4 형식을 체크하는 함수를 구현하면 다음과 같다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <regex>
using namespace std;
bool isValidIPv4(const string& ip)
{
regex pattern(R"(\b(?:\d{1,3}\.){3}\d{1,3}\b)");
return regex_match(ip, pattern);
}
int main()
{
string IP1 = "192.168.1.1";
string IP2 = "192.168.X.X";
bool isValid1 = isValidIPv4(IP1);
bool isValid2 = isValidIPv4(IP2);
cout << IP1 << " : " << isValid1 << endl; // true
cout << IP2 << " : " << isValid2 << endl; // false
return 0;
}
IPv4 정규 표현식 : \b(?:\d{1,3}\.){3}\d{1,3}\b
정규 표현식 \b는 단어의 경계(시작과 끝)를 나타낸다.
(?:\d{1,3}\.){3} 는 숫자가 1개 ~ 3개가 나온 후, "." 이 나오는 패턴이 3번 반복됨을 의미한다.
\d{1,3} 는 마지막 숫자 1개 ~ 3개를 의미한다.
위와 같은 구현대로라면 999.999.999.999의 경우도 true가 나온다.
좀 더 구체적으로 "." 을 split 해서 각 숫자가 255 이하인지 확인하는 절차가 필요하지만, 여기서는 생략한다.
IPv6 Invalid Check (+ 축약형)
위와 같은 방법으로 IPv6 형식을 체크해 보자.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <regex>
using namespace std;
bool isValidIPv6(const string& ip)
{
regex pattern(R"(\b(?:[A-Fa-f0-9]{1,4}:){7}[A-Fa-f0-9]{1,4}\b)");
return regex_match(ip, pattern);
}
int main()
{
string IP1 = "192.168.1.1";
string IP2 = "2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334";
string IP3 = "2001:0db8:85a3:::8a2e:0370:7334"; // 축약형
bool isValid1 = isValidIPv6(IP1);
bool isValid2 = isValidIPv6(IP2);
bool isValid3 = isValidIPv6(IP3);
cout << IP1 << " : " << isValid1 << endl; // false
cout << IP2 << " : " << isValid2 << endl; // true
cout << IP3 << " : " << isValid3 << endl; // false
return 0;
}
위의 경우 축약형으로 나타낸 경우는 false가 나타난다.
아래와 같이 정규식을 변경하면 모두 정상적으로 동작한다.
//regex pattern(R"(\b(?:[A-Fa-f0-9]{1,4}:){7}[A-Fa-f0-9]{1,4}\b)");
regex pattern(R"(\b(::)?[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}(:[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}){0,7}\b)");
IPv6 정규 표현식 : \b(::)?[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}(:[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}){0,7}\b
(::)?는 "::" 패턴을 옵션으로 포함하며, 선택사항을 의미한다.
축약형도 정상적으로 동작하는지 확인해 보자.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <regex>
using namespace std;
bool isValidIPv6(const string& ip)
{
regex pattern(R"(\b(::)?[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}(:[A-Fa-f0-9]{0,4}){0,7}\b)");
return regex_match(ip, pattern);
}
int main()
{
string IP1 = "192.168.1.1";
string IP2 = "2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334";
string IP3 = "2001:0db8:85a3:::8a2e:0370:7334"; // 축약형
bool isValid1 = isValidIPv6(IP1);
bool isValid2 = isValidIPv6(IP2);
bool isValid3 = isValidIPv6(IP3);
cout << IP1 << " : " << isValid1 << endl; // false
cout << IP2 << " : " << isValid2 << endl; // true
cout << IP3 << " : " << isValid3 << endl; // true
return 0;
}Integer to IPv4 String
unsigned int는 32비트이고 각 8비트가 IPv4의 최대 세 자릿수를 나타낸다.
비트 연산을 이용하여 아래와 같이 구현할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string ipv4ToString(unsigned int ipv4)
{
string result = to_string((ipv4 >> 24) & 0xFF) + "." +
to_string((ipv4 >> 16) & 0xFF) + "." +
to_string((ipv4 >> 8) & 0xFF) + "." +
to_string(ipv4 & 0xFF);
return result;
}
int main()
{
unsigned int ipv4Address = 3232235777;
string ipv4String = ipv4ToString(ipv4Address);
cout << ipv4Address << " > " << ipv4String << endl; // 192.168.1.1
return 0;
}IPv4 String to Integer
IPv4 string을 스트림 형태로 변경하여 처리한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
unsigned int ipv4ToInt(const string& ipv4)
{
istringstream iss(ipv4);
string token;
vector<unsigned int> octets;
while (getline(iss, token, '.'))
octets.push_back(stoi(token));
if (octets.size() != 4)
{
cerr << "Invalid IPv4 format" << endl;
return 0;
}
return (octets[0] << 24) | (octets[1] << 16) | (octets[2] << 8) | octets[3];
}
int main()
{
string ipv4Address = "192.168.1.1";
unsigned int intIPv4 = ipv4ToInt(ipv4Address);
cout << ipv4Address << " > " << intIPv4 << endl; // 3232235777
return 0;
}
C++ Split을 이용해서 구현할 수도 있지만 여기서는 생략한다.
IPv4 String to Integer / Integer to IPv4 String with <arpa/inet.h>
<arpa/inet.h> 헤더를 이용하면 IP와 관련된 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
이 헤더는 window 비주얼 스튜디오에서는 제공하지 않으므로, replit에서 코드를 실행하자.
inet_pton으로 IPv4 주소를 네트워크 바이트 순서로 변환한다.
그리고 ntohl을 이용하면 in_addr을 unsigned_int로 변경할 수 있다.
반대의 경우는 htonl을 사용한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
using namespace std;
unsigned int ipv4ToInt(const string& ipAddress)
{
struct in_addr addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET, ipAddress.c_str(), &addr);
return ntohl(addr.s_addr);
}
string intToIPv4(unsigned int value)
{
struct in_addr addr;
char ip[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
addr.s_addr = htonl(value);
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &(addr.s_addr), ip, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
return string(ip);
}
int main()
{
string IP1 = "7.91.205.21";
string IP2 = "255.255.255.255";
unsigned int value1 = 123456789;
unsigned int value2 = 4294967295;
cout << IP1 << " > " << ipv4ToInt(IP1) << endl;
cout << IP2 << " > " << ipv4ToInt(IP2) << endl;
cout << value1 << " > " << intToIPv4(value1) << endl;
cout << value2 << " > " << intToIPv4(value2) << endl;
return 0;
}
in_addr to IPv4 String / IPv4 String to in_addr with <arpa/inet.h>
in_addr 타입을 string으로 또는 string을 in_addr로 변환하는 방법은 아래와 같다.
in_addr 출력을 위해 연산자 오버로딩을 이용하였다. (inet_ntoa : in_addr을 IPv4 문자열로 변환)
참고로 변환이 성공하는 경우 inet_pton은 1을 return 한다.
여기서는 모두 변환이 가능하다고 가정하였다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
using namespace std;
unsigned int ipv4ToInt(const string& ipAddress)
{
struct in_addr addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET, ipAddress.c_str(), &addr);
return ntohl(addr.s_addr);
}
in_addr stringToInAddr(const string& ipAddress)
{
in_addr addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET, ipAddress.c_str(), &addr);
return addr;
}
string inAddrToString(const in_addr& ipv4Address)
{
return string(inet_ntoa(ipv4Address));
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const in_addr& ipv4Address)
{
os << inAddrToString(ipv4Address);
return os;
}
int main()
{
string ipv4String = "192.168.1.1";
in_addr ipv4Address = stringToInAddr(ipv4String);
cout << "ipv4Address : " << ipv4Address << endl;
cout << "ipv4Address.s_addr : " << ipv4Address.s_addr << endl;
cout << "ipv4Address to Int : " << ipv4ToInt(ipv4String) << endl;
return 0;
}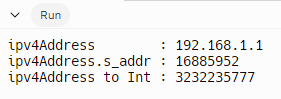
in_addr의 s_addr은 네트워크 바이트 순서로 변환하기 전 int 값이기 때문에 IP 값이 거꾸로 나오게 된다.
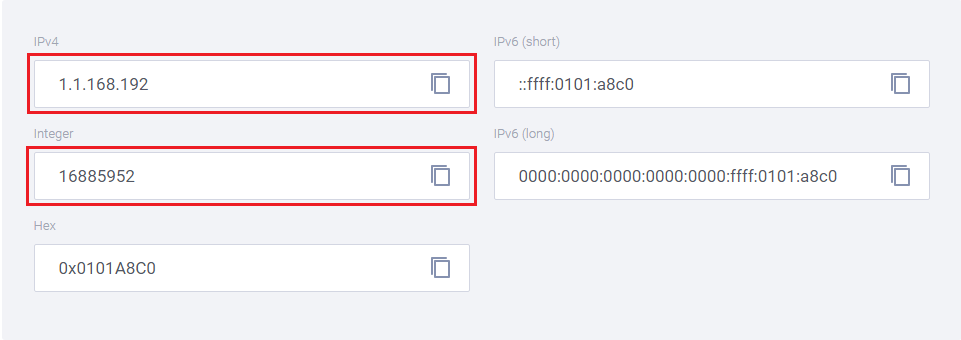
inet_ntoa 대신 inet_ntop를 사용할 수 있다.
inet_ntop는 변환에 실패하면 NULL을 return 한다.
NULL check 코드는 생략하였다.
string inAddrToString(const in_addr& ipv4Address)
{
char buffer[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &ipv4Address, buffer, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
return string(buffer);
}in6_addr to IPv6 String / IPv6 String to in6_addr with <arpa/inet.h>
마찬가지로 inet_pton과 inet_ntop을 이용해서 변환할 수 있다. (inet_ntoa는 IPv4 주소만 처리 가능하다.)
여기서도 모두 변환이 가능하다고 가정하였다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
using namespace std;
in6_addr stringToIn6Addr(const string& ipAddress)
{
in6_addr addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET6, ipAddress.c_str(), &addr);
return addr;
}
string in6AddrToString(const in6_addr& ipv6Address)
{
char buffer[INET6_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &ipv6Address, buffer, INET6_ADDRSTRLEN);
return string(buffer);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const in6_addr& ipv6Address)
{
os << in6AddrToString(ipv6Address);
return os;
}
int main()
{
string ipv6String = "2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334";
in6_addr ipv6Address = stringToIn6Addr(ipv6String);
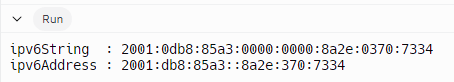
cout << "ipv6String : " << ipv6String << endl;
cout << "ipv6Address : " << ipv6Address << endl;
return 0;
}
IPv4 to IPv6 with <arpa/inet.h>
IPv4를 IPv6로 아래와 같이 바꿀 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
using namespace std;
string ipv4ToIPv6(const string& ipv4)
{
struct in6_addr v6addr;
struct in_addr v4addr;
inet_pton(AF_INET, ipv4.c_str(), &v4addr);
memset(&v6addr, 0, sizeof(struct in6_addr));
v6addr.s6_addr[10] = 0xFF;
v6addr.s6_addr[11] = 0xFF;
memcpy(&v6addr.s6_addr[12], &v4addr.s_addr, sizeof(v4addr.s_addr));
char ipv6[INET6_ADDRSTRLEN];
inet_ntop(AF_INET6, &v6addr, ipv6, sizeof(ipv6));
return string(ipv6);
}
int main()
{
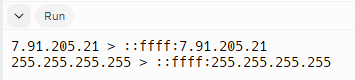
string IPv4_1 = "7.91.205.21";
string IPv4_2 = "255.255.255.255";
cout << IPv4_1 << " > " << ipv4ToIPv6(IPv4_1) << endl;
cout << IPv4_2 << " > " << ipv4ToIPv6(IPv4_2) << endl;
return 0;
}
'개발 > C, C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ - atomic으로 원자적 연산 처리하기 (vs mutex) (0) | 2024.01.26 |
|---|---|
| C++ - call_once로 함수를 한 번만 호출하기 (0) | 2024.01.24 |
| C++ - 연산자 오버로딩을 이용하여 구조체 출력하기 (cout with overloading) (0) | 2023.11.22 |
| C++ - map, functional로 함수 호출하기 (0) | 2023.11.22 |
| C++ - 폴더, 파일 관리 함수 정리 with sys/stat.h, dirent.h, fstream (0) | 2023.09.09 |




댓글