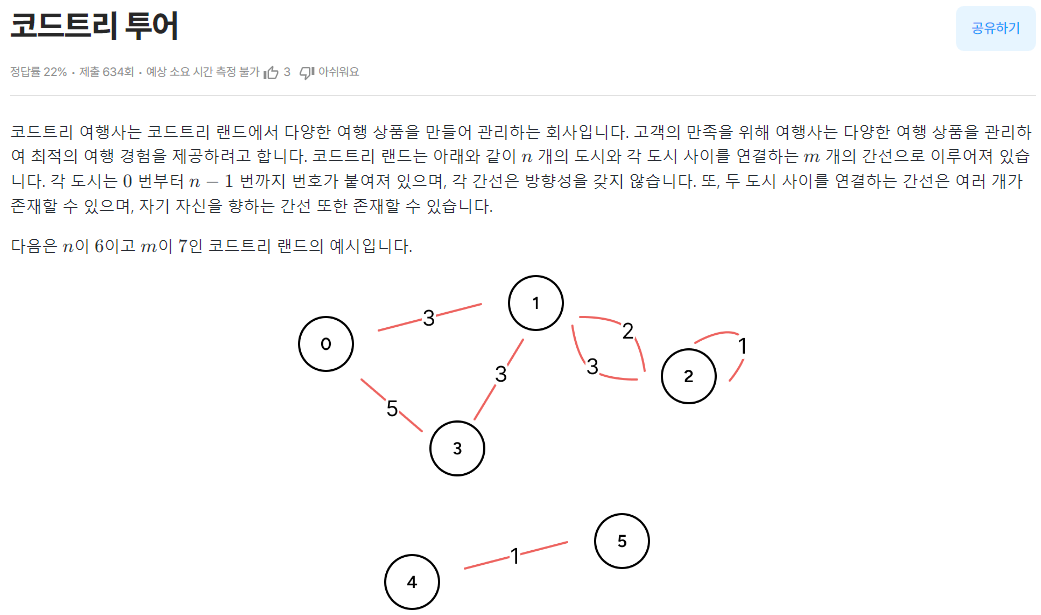
[코드트리] 코드트리 투어 (삼성 SW 역량테스트 2024 상반기 오전 2번, B형)
SW 역량테스트 합격하기 A형 강의 오픈!! (인프런 바로가기)
2022 하반기 이후 문제 풀이 시간이 3시간 → 4시간으로 변경,
A형 1문제 + B형 문제 1문제가 출제됩니다.
참고
- B형 필수 : 우선순위 큐 Priority Queue
https://www.codetree.ai/training-field/frequent-problems/problems/codetree-tour
코드트리 랜드 건설
모든 도시에 대해 가중치를 INF(= 0x7fff0000)으로 초기화한다.
최소거리를 구하는 문제이므로, 여러 간선 중 최소의 가중치만 필요하다.
따라서 가장 작은 가중치만 W[v][u] / W[u][v]에 저장한다.
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
W[i][k] = INF;
for (int m = 0; m < M; m++)
{
int v, u, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &u, &w);
if (w < W[v][u]) W[v][u] = w;
if (w < W[u][v]) W[u][v] = w;
}
가중치가 입력되었다면 필요한 가중치만 다시 2차원 배열에 만든다.
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
wIndex[i] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
if (W[i][k] == INF) continue;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]].value = k;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]++].weight = W[i][k];
}
}
가중치 입력이 완료되었으면 다익스트라를 실행한다.
dijkstra();
input은 다음과 같다.
#define MAX (2000 + 50)
...
#define INF (0x7fff0000)
int W[MAX][MAX];
typedef struct st1
{
int value;
int weight;
}NODE;
NODE wNode[MAX][MAX];
int wIndex[MAX];
void input()
{
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
START = 0;
thn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
W[i][k] = INF;
for (int m = 0; m < M; m++)
{
int v, u, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &u, &w);
if (w < W[v][u]) W[v][u] = w;
if (w < W[u][v]) W[u][v] = w;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
wIndex[i] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
if (W[i][k] == INF) continue;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]].value = k;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]++].weight = W[i][k];
}
}
dijkstra();
}
다익스트라가 완료되면 START에서 각 도시별로 최소 거리를 DISTANCE[도시 번호]로 구할 수 있다.
이때, heap의 크기는 간선의 개수만큼 선언해야 한다.
int START;
int DISTANCE[MAX];
typedef struct st2
{
int node;
int weight;
}EDGE;
EDGE heap[10000 + 500]; // MAX_M
int hn;
EDGE pop()
{
int i;
EDGE ret, tmp;
ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap[hn];
heap[hn--].weight = INF;
for (i = 1; i * 2 <= hn;)
{
if (heap[i].weight < heap[i * 2].weight && heap[i].weight < heap[i * 2 + 1].weight) break;
if (heap[i * 2].weight < heap[i * 2 + 1].weight)
{
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i * 2];
heap[i * 2] = tmp;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i * 2 + 1];
heap[i * 2 + 1] = tmp;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
void push(EDGE x)
{
int i;
EDGE tmp;
heap[++hn] = x;
for (i = hn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (heap[i / 2].weight < heap[i].weight) break;
tmp = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
}
}
void dijkstra()
{
int visit[MAX] = { 0 };
hn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) DISTANCE[i] = INF;
DISTANCE[START] = 0;
push({ START, 0 });
while (hn)
{
EDGE tmp;
tmp = pop();
if (visit[tmp.node]) continue;
visit[tmp.node] = 1;
int nodeNum = tmp.node;
int index = wIndex[tmp.node];
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
NODE nd = wNode[nodeNum][i];
// printf("nodeNum %d %d %d %d\n", nodeNum, i, nd.value, nd.weight);
if (DISTANCE[nd.value] > DISTANCE[tmp.node] + nd.weight)
{
DISTANCE[nd.value] = DISTANCE[tmp.node] + nd.weight;
push({ nd.value, DISTANCE[nd.value] });
}
}
}
// printf("START %d\n", START);
// for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("distance : %d\n", DISTANCE[i]);
}여행 상품 생성
여행 상품은 두 경우로 나눈다.
travel.profit이 음수인 경우, IMPOSSIBLE_LIST에 넣고,
travel.profit이 0 이상인 경우, 우선순위 큐에 넣는다.
profit은 revenue에서 거리를 빼서 구할 수 있다.
여행 상품이 생성될 때, travelStatus를 AVAILABLE로 갱신한다.
void create(int id, int revenue, int dest)
{
TRAVEL travel = { 0 };
travelStatus[id] = AVAILABLE;
travel.id = id;
travel.revenue = revenue;
travel.dest = dest;
travel.profit = revenue - DISTANCE[dest];
if (travel.profit < 0)
IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[ipidx++] = travel;
else
pushTravel(travel);
}
여행 상품은 profit이 클수록, id가 작을수록 우선순위가 높다.
따라서 우선순위 큐는 다음과 같이 구현한다.
typedef struct st3
{
int id;
int revenue;
int dest;
int profit;
}TRAVEL;
int travelStatus[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
TRAVEL TRAVEL_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
TRAVEL IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID]; // 도달 불가 상품, 이득을 얻을 수 없는 상품
TRAVEL TEMP_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
int ipidx;
TRAVEL heapTravel[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
int thn;
int isPriority(TRAVEL a, TRAVEL b)
{
if (a.profit != b.profit) return a.profit > b.profit;
return a.id < b.id;
}
TRAVEL popTravel()
{
int i;
TRAVEL ret, tmp;
ret = heapTravel[1];
heapTravel[1] = heapTravel[thn];
heapTravel[thn].id = INF;
heapTravel[thn--].profit = -INF;
for (i = 1; i * 2 <= thn;)
{
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i], heapTravel[i * 2]) && isPriority(heapTravel[i], heapTravel[i * 2 + 1])) break;
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i * 2], heapTravel[i * 2 + 1]))
{
tmp = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = heapTravel[i * 2];
heapTravel[i * 2] = tmp;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = heapTravel[i * 2 + 1];
heapTravel[i * 2 + 1] = tmp;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
void pushTravel(TRAVEL x)
{
int i;
TRAVEL tmp;
heapTravel[++thn] = x;
for (i = thn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i / 2], heapTravel[i])) break;
tmp = heapTravel[i / 2];
heapTravel[i / 2] = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = tmp;
}
}여행 상품 취소
travelStatus를 NOT_USED로 갱신한다.
여행 상품이 취소되더라도 우선순위 큐에서 뺄 필요가 없다.
void cancel(int id)
{
travelStatus[id] = NOT_USED;
}최적의 여행 상품 판매
우선순위 큐에서 가장 우선순위가 높은 상품을 판매하면 된다.
이때, 취소된 여행 상품이라면 다시 pop을 하면 된다.
즉, 관리 목록이 존재하는 경우(whn != 0), 취소된 상품이 아닐 때까지 pop을 하면 된다.
void sold()
{
while (thn)
{
TRAVEL out = popTravel();
if (travelStatus[out.id] == NOT_USED) continue;
travelStatus[out.id] = NOT_USED;
printf("%d\n", out.id);
return;
}
printf("-1\n");
}여행 상품의 출발지 변경
출발지를 변경하고 다익스트라를 다시 실행한다.
우선순위 큐에 있던 관리 목록과 불가 목록을 TEMP_LIST로 옮긴다.
출발지 변경으로 인해 관리 목록에 있는 여행 상품이 불가로 이동할 수도 있고,
반대로 불가 목록이 가능한 여행이 될 수 있다.
취소된 여행을 제외하고, profit을 다시 계산해서 불가 목록이나 관리 목록에 분류하면 된다.
void change(int s)
{
START = s;
dijkstra();
int tempIndex = 0;
// HEAP에 있는 여행 정보를 모두 임시 목록에 추가
for (int i = 1; i <= thn; i++) TEMP_LIST[tempIndex++] = heapTravel[i];
// 도달 불가 상품, 이득을 얻을 수 없는 상품도 임시 목록에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < ipidx; i++) TEMP_LIST[tempIndex++] = IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[i];
thn = ipidx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempIndex; i++)
{
TRAVEL t = TEMP_LIST[i];
if (travelStatus[t.id] == NOT_USED) continue;
t.profit = t.revenue - DISTANCE[t.dest];
if (t.profit < 0)
IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[ipidx++] = t;
else
pushTravel(t);
}
}전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX (2000 + 50)
#define MAX_TRAVEL_ID (30000 + 500)
#define BUILD (100)
#define CREATE (200)
#define CANCEL (300)
#define SOLD (400)
#define CHANGE (500)
#define INF (0x7fff0000)
#define AVAILABLE (0)
#define NOT_USED (1)
int N, M;
/* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// 다익스트라
int W[MAX][MAX];
typedef struct st1
{
int value;
int weight;
}NODE;
NODE wNode[MAX][MAX];
int wIndex[MAX];
int START;
int DISTANCE[MAX];
typedef struct st2
{
int node;
int weight;
}EDGE;
EDGE heap[10000 + 500]; // MAX_M
int hn;
EDGE pop()
{
int i;
EDGE ret, tmp;
ret = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap[hn];
heap[hn--].weight = INF;
for (i = 1; i * 2 <= hn;)
{
if (heap[i].weight < heap[i * 2].weight && heap[i].weight < heap[i * 2 + 1].weight) break;
if (heap[i * 2].weight < heap[i * 2 + 1].weight)
{
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i * 2];
heap[i * 2] = tmp;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[i * 2 + 1];
heap[i * 2 + 1] = tmp;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
void push(EDGE x)
{
int i;
EDGE tmp;
heap[++hn] = x;
for (i = hn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (heap[i / 2].weight < heap[i].weight) break;
tmp = heap[i / 2];
heap[i / 2] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
}
}
void dijkstra()
{
int visit[MAX] = { 0 };
hn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) DISTANCE[i] = INF;
DISTANCE[START] = 0;
push({ START, 0 });
while (hn)
{
EDGE tmp;
tmp = pop();
if (visit[tmp.node]) continue;
visit[tmp.node] = 1;
int nodeNum = tmp.node;
int index = wIndex[tmp.node];
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
NODE nd = wNode[nodeNum][i];
// printf("nodeNum %d %d %d %d\n", nodeNum, i, nd.value, nd.weight);
if (DISTANCE[nd.value] > DISTANCE[tmp.node] + nd.weight)
{
DISTANCE[nd.value] = DISTANCE[tmp.node] + nd.weight;
push({ nd.value, DISTANCE[nd.value] });
}
}
}
// printf("START %d\n", START);
// for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("distance : %d\n", DISTANCE[i]);
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// 관리 목록
typedef struct st3
{
int id;
int revenue;
int dest;
int profit;
}TRAVEL;
int travelStatus[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
TRAVEL TRAVEL_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
TRAVEL IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID]; // 도달 불가 상품, 이득을 얻을 수 없는 상품
TRAVEL TEMP_LIST[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
int ipidx;
TRAVEL heapTravel[MAX_TRAVEL_ID];
int thn;
int isPriority(TRAVEL a, TRAVEL b)
{
if (a.profit != b.profit) return a.profit > b.profit;
return a.id < b.id;
}
TRAVEL popTravel()
{
int i;
TRAVEL ret, tmp;
ret = heapTravel[1];
heapTravel[1] = heapTravel[thn];
heapTravel[thn].id = INF;
heapTravel[thn--].profit = -INF;
for (i = 1; i * 2 <= thn;)
{
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i], heapTravel[i * 2]) && isPriority(heapTravel[i], heapTravel[i * 2 + 1])) break;
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i * 2], heapTravel[i * 2 + 1]))
{
tmp = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = heapTravel[i * 2];
heapTravel[i * 2] = tmp;
i = i * 2;
}
else
{
tmp = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = heapTravel[i * 2 + 1];
heapTravel[i * 2 + 1] = tmp;
i = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
void pushTravel(TRAVEL x)
{
int i;
TRAVEL tmp;
heapTravel[++thn] = x;
for (i = thn; i > 1; i /= 2)
{
if (isPriority(heapTravel[i / 2], heapTravel[i])) break;
tmp = heapTravel[i / 2];
heapTravel[i / 2] = heapTravel[i];
heapTravel[i] = tmp;
}
}
void input()
{
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
START = 0;
thn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
W[i][k] = INF;
for (int m = 0; m < M; m++)
{
int v, u, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &v, &u, &w);
if (w < W[v][u]) W[v][u] = w;
if (w < W[u][v]) W[u][v] = w;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
wIndex[i] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
if (W[i][k] == INF) continue;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]].value = k;
wNode[i][wIndex[i]++].weight = W[i][k];
}
}
dijkstra();
}
void printNode(int index)
{
printf("index : %d / ", index);
for (int i = 0; i < wIndex[index]; i++) printf("(v %d, w %d)", wNode[index][i].value, wNode[index][i].weight);
putchar('\n');
}
void printNodeAll()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) printNode(i);
putchar('\n');
}
void create(int id, int revenue, int dest)
{
TRAVEL travel = { 0 };
travelStatus[id] = AVAILABLE;
travel.id = id;
travel.revenue = revenue;
travel.dest = dest;
travel.profit = revenue - DISTANCE[dest];
if (travel.profit < 0)
IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[ipidx++] = travel;
else
pushTravel(travel);
}
void cancel(int id)
{
travelStatus[id] = NOT_USED;
}
void sold()
{
while (thn)
{
TRAVEL out = popTravel();
if (travelStatus[out.id] == NOT_USED) continue;
travelStatus[out.id] = NOT_USED;
printf("%d\n", out.id);
return;
}
printf("-1\n");
}
void change(int s)
{
START = s;
dijkstra();
int tempIndex = 0;
// HEAP에 있는 여행 정보를 모두 임시 목록에 추가
for (int i = 1; i <= thn; i++) TEMP_LIST[tempIndex++] = heapTravel[i];
// 도달 불가 상품, 이득을 얻을 수 없는 상품도 임시 목록에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < ipidx; i++) TEMP_LIST[tempIndex++] = IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[i];
thn = ipidx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempIndex; i++)
{
TRAVEL t = TEMP_LIST[i];
if (travelStatus[t.id] == NOT_USED) continue;
t.profit = t.revenue - DISTANCE[t.dest];
if (t.profit < 0)
IMPOSSIBLE_LIST[ipidx++] = t;
else
pushTravel(t);
}
}
int main()
{
int Q;
scanf("%d", &Q);
for (int q = 0; q < Q; q++)
{
int COMMAND;
scanf("%d", &COMMAND);
if (COMMAND == BUILD) input();
else if (COMMAND == CREATE)
{
int id, revenue, dest;
scanf("%d %d %d", &id, &revenue, &dest);
create(id, revenue, dest);
}
else if (COMMAND == CANCEL)
{
int id;
scanf("%d", &id);
cancel(id);
}
else if (COMMAND == SOLD)
{
sold();
}
else if (COMMAND == CHANGE)
{
int s;
scanf("%d", &s);
change(s);
}
}
return 0;
}