[코드트리] 마법의 숲 탐색 (삼성 SW 역량테스트 2024 상반기 오후 1번)
A형 필수 알고리즘을 체계적으로 배우고 싶다면? (인프런 바로가기)
https://www.codetree.ai/training-field/frequent-problems/problems/magical-forest-exploration
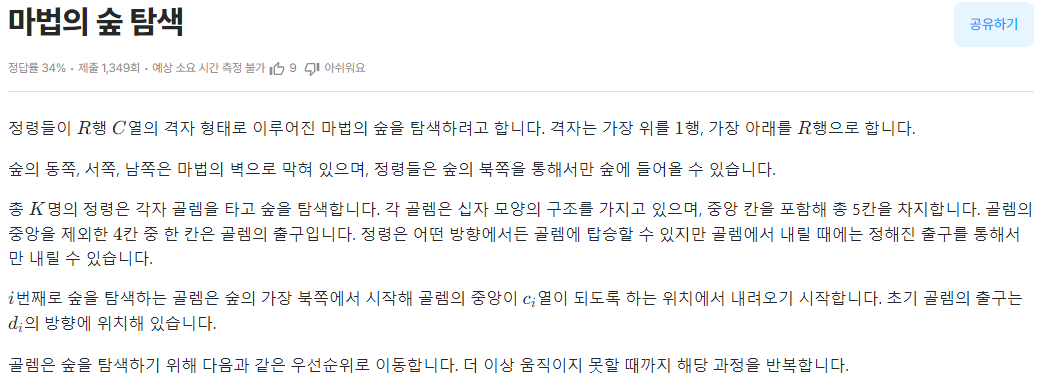
2차원 배열 좌표와 GOLEM을 위한 좌표를 관리하기 위한 구조체를 선언한다.
typedef struct st1
{
int r;
int c;
}RC;
typedef struct st2
{
int r;
int c;
int dir;
int id;
}GOLEM;
골렘의 몸통, 중심, 출구를 구분하기 위해 define을 정의한다. (= 타입)
그리고 골렘의 ID에 100 (= MARK)을 곱해서 MAP에 표시하여 각 골렘을 구분한다. (아래 구현 참고)
#define BODY (1)
#define CENTER (2)
#define EXIT (3)
#define MARK (100)
2차원 배열을 탐색하기 위한 배열을 선언한다.
// 북동남서 ↑, →, ↓, ←
int dr[] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
int dc[] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
input은 다음과 같다.
void input()
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &R, &C, &K);
}
골렘을 MAP에 표시하기 위한 함수를 만든다.
MAP에는 골렘의 ID와 타입(몸통, 중심, 출구)을 더하여 저장한다.
골렘의 ID는 주어지는 순서대로 1부터 시작하지만 setGolem에 들어올 때는 100이 곱한 값이 들어온다.
void clearMAP()
{
for (int r = 0; r < MAX; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < MAX; c++)
MAP[r][c] = 0;
}
void setGolem(GOLEM g)
{
MAP[g.r][g.c] = CENTER + g.id;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nr, nc;
nr = g.r + dr[i];
nc = g.c + dc[i];
MAP[nr][nc] = BODY + g.id;
}
MAP[g.r + dr[g.dir]][g.c + dc[g.dir]] = EXIT + g.id;
}
main은 다음과 같다.
골렘의 ID는 MARK(100)를 곱해둔다.
그리고 각 골렘별로 simulate를 실행한다.
int main()
{
// scanf("%d", &T);
T = 1;
for (int tc = 1; tc <= T; tc++)
{
input();
clearMAP();
int answer = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= K; k++)
{
int c, d;
scanf("%d %d", &c, &d);
GOLEM g;
g.r = 1;
g.c = c;
g.dir = d;
g.id = k * MARK;
int score = simulate(g);
answer += score;
}
printf("%d\n", answer);
}
return 0;
}시뮬레이션
시뮬레이션은 다음과 같다.
1) 주어진 요구대로 남쪽 / 서쪽 / 동쪽으로 움직인다.
2) 몸의 일부가 벗어나는 경우 (골렘의 중심 행이 3 이하), 골렘을 MAP에서 모두 제거한다. (clearMap)
3) 그렇지 않은 경우는 골렘을 MAP에 표시한다. (setGolem)
4) BFS를 이용해 가장 남쪽으로 이동할 수 있는 좌표의 행을 구해서 return 한다. (2를 뺀다.)
int simulate(GOLEM g)
{
// 계속 움직이기
while (1)
{
if (checkSouth(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
}
else if (checkWest(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
g.c = g.c - 1;
g.dir = (g.dir + 4 - 1) % 4;
}
else if (checkEast(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
g.c = g.c + 1;
g.dir = (g.dir + 1) % 4;
}
else
break;
}
// map을 초과하는 경우 reset
if (g.r <= 3)
{
clearMAP();
return 0;
}
// 그렇지 않은 경우 점수 계산
// MAP 표시 후
setGolem(g);
return (BFS(g) - 2); // 행 조정
}
골렘을 쉽게 내려오게 하기 위해 행 좌표를 2 증가시키고, 값을 구할 때 2를 빼는 방법을 사용한다.
남쪽으로 이동할 수 있는지 여부는 다음과 같이 확인할 수 있다. (행 좌표가 조정 중이라는 것에 유의)
문제에서 요구하는 이동할 공간이 모두 빈 공간인 경우 이동할 수 있도록 하였다.
// 남쪽
int checkSouth(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.r == R + 3 - 2) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r + 1;
r[1] = g.r + 2;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c - 1;
c[1] = g.c;
c[2] = g.c + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
서쪽은 왼쪽을, 동쪽은 오른쪽을 확인한다.
이후 다시 남쪽 코드를 return하면 된다.
// 서쪽
int checkWest(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.c == 2) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r - 1;
r[1] = g.r;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c - 1;
c[1] = g.c - 2;
c[2] = g.c - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
GOLEM tempGolem = { 0 };
tempGolem.r = g.r;
tempGolem.c = g.c - 1;
return checkSouth(tempGolem);
}
// 동쪽
int checkEast(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.c == C - 1) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r - 1;
r[1] = g.r;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c + 1;
c[1] = g.c + 2;
c[2] = g.c + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
GOLEM tempGolem = { 0 };
tempGolem.r = g.r;
tempGolem.c = g.c + 1;
return checkSouth(tempGolem);
}
골렘이 움직일 수 있는 모든 영역을 BFS로 탐색한다.
움직일 수 있는 영역의 가장 큰 행을 갱신한다.
RC out = queue[rp++];
if (maxR < out.r) maxR = out.r;
이때, 골렘은 다른 골렘의 영역을 이동할 때는 출구와 붙어 있는 경우만 이동이 가능하다.
골렘의 영역은 golemID에 100을 곱하였고 type을 더하였었다.
따라서 다시 골렘의 ID와 타입을 나누기와 나머지 연산으로 분리할 수 있다.
int golemID = (MAP[out.r][out.c] / MARK) * MARK;
int type = MAP[out.r][out.c] % MARK;
그러면 다음 좌표에서 출구가 아니면서 골렘의 ID가 다른 경우는 탐색하지 않도록 처리할 수 있다.
// 출구가 아니고 id가 다른 경우는 이동 불가
if (golemID != nGolemID && type != EXIT) continue;
전체 BFS 코드는 다음과 같다.
int BFS(GOLEM g)
{
RC queue[MAX * MAX] = { 0 };
int rp, wp;
int visit[MAX][MAX] = { 0 };
rp = wp = 0;
queue[wp].r = g.r;
queue[wp++].c = g.c;
int maxR = 0;
while (rp < wp)
{
RC out = queue[rp++];
if (maxR < out.r) maxR = out.r;
int golemID = (MAP[out.r][out.c] / MARK) * MARK;
int type = MAP[out.r][out.c] % MARK;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nr, nc;
nr = out.r + dr[i];
nc = out.c + dc[i];
if (nr < 1 || nc < 1 || nr >(R + 3) || nc > C) continue;
// 0인 공간, 방문한 공간은 이동 불가
if (MAP[nr][nc] == 0 || visit[nr][nc]) continue;
int nGolemID = (MAP[nr][nc] / MARK) * MARK;
// 출구가 아니고 id가 다른 경우는 이동 불가
if (golemID != nGolemID && type != EXIT) continue;
queue[wp].r = nr;
queue[wp++].c = nc;
visit[nr][nc] = 1;
}
}
return maxR;
}전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX (70 + 10)
int T;
int R, C, K;
#define BODY (1)
#define CENTER (2)
#define EXIT (3)
#define MARK (100)
typedef struct st1
{
int r;
int c;
}RC;
typedef struct st2
{
int r;
int c;
int dir;
int id;
}GOLEM;
// 북동남서 ↑, →, ↓, ←
int dr[] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
int dc[] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
int MAP[MAX][MAX];
void printMAP(GOLEM g)
{
int temp[MAX][MAX] = { 0 };
for (int r = 0; r < MAX; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < MAX; c++)
temp[r][c] = MAP[r][c];
temp[g.r][g.c] = CENTER;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nr, nc;
nr = g.r + dr[i];
nc = g.c + dc[i];
temp[nr][nc] = BODY;
}
temp[g.r + dr[g.dir]][g.c + dc[g.dir]] = EXIT;
for (int r = 0; r < R + 3; r++)
{
for (int c = 1; c <= C; c++)
printf("%d ", temp[r][c]);
putchar('\n');
}
putchar('\n');
}
void input()
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &R, &C, &K);
}
void clearMAP()
{
for (int r = 0; r < MAX; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < MAX; c++)
MAP[r][c] = 0;
}
void setGolem(GOLEM g)
{
MAP[g.r][g.c] = CENTER + g.id;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nr, nc;
nr = g.r + dr[i];
nc = g.c + dc[i];
MAP[nr][nc] = BODY + g.id;
}
MAP[g.r + dr[g.dir]][g.c + dc[g.dir]] = EXIT + g.id;
}
// 남쪽
int checkSouth(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.r == R + 3 - 2) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r + 1;
r[1] = g.r + 2;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c - 1;
c[1] = g.c;
c[2] = g.c + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
// 서쪽
int checkWest(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.c == 2) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r - 1;
r[1] = g.r;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c - 1;
c[1] = g.c - 2;
c[2] = g.c - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
GOLEM tempGolem = { 0 };
tempGolem.r = g.r;
tempGolem.c = g.c - 1;
return checkSouth(tempGolem);
}
// 동쪽
int checkEast(GOLEM g)
{
if (g.c == C - 1) return 0;
int r[3] = { 0 };
int c[3] = { 0 };
r[0] = g.r - 1;
r[1] = g.r;
r[2] = g.r + 1;
c[0] = g.c + 1;
c[1] = g.c + 2;
c[2] = g.c + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (MAP[r[i]][c[i]] != 0) return 0;
GOLEM tempGolem = { 0 };
tempGolem.r = g.r;
tempGolem.c = g.c + 1;
return checkSouth(tempGolem);
}
int BFS(GOLEM g)
{
RC queue[MAX * MAX] = { 0 };
int rp, wp;
int visit[MAX][MAX] = { 0 };
rp = wp = 0;
queue[wp].r = g.r;
queue[wp++].c = g.c;
int maxR = 0;
while (rp < wp)
{
RC out = queue[rp++];
if (maxR < out.r) maxR = out.r;
int golemID = (MAP[out.r][out.c] / MARK) * MARK;
int type = MAP[out.r][out.c] % MARK;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nr, nc;
nr = out.r + dr[i];
nc = out.c + dc[i];
if (nr < 1 || nc < 1 || nr >(R + 3) || nc > C) continue;
// 0인 공간, 방문한 공간은 이동 불가
if (MAP[nr][nc] == 0 || visit[nr][nc]) continue;
int nGolemID = (MAP[nr][nc] / MARK) * MARK;
// 출구가 아니고 id가 다른 경우는 이동 불가
if (type != EXIT && golemID != nGolemID ) continue;
queue[wp].r = nr;
queue[wp++].c = nc;
visit[nr][nc] = 1;
}
}
return maxR;
}
int simulate(GOLEM g)
{
// 계속 움직이기
while (1)
{
if (checkSouth(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
}
else if (checkWest(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
g.c = g.c - 1;
g.dir = (g.dir + 4 - 1) % 4;
}
else if (checkEast(g))
{
g.r = g.r + 1;
g.c = g.c + 1;
g.dir = (g.dir + 1) % 4;
}
else
break;
}
// map을 초과하는 경우 reset
if (g.r <= 3)
{
clearMAP();
return 0;
}
// 그렇지 않은 경우 점수 계산
// MAP 표시 후
setGolem(g);
return (BFS(g) - 2); // 행 조정
}
int main()
{
// scanf("%d", &T);
T = 1;
for (int tc = 1; tc <= T; tc++)
{
input();
clearMAP();
int answer = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= K; k++)
{
int c, d;
scanf("%d %d", &c, &d);
GOLEM g;
g.r = 1;
g.c = c;
g.dir = d;
g.id = k * MARK;
int score = simulate(g);
answer += score;
}
printf("%d\n", answer);
}
return 0;
}